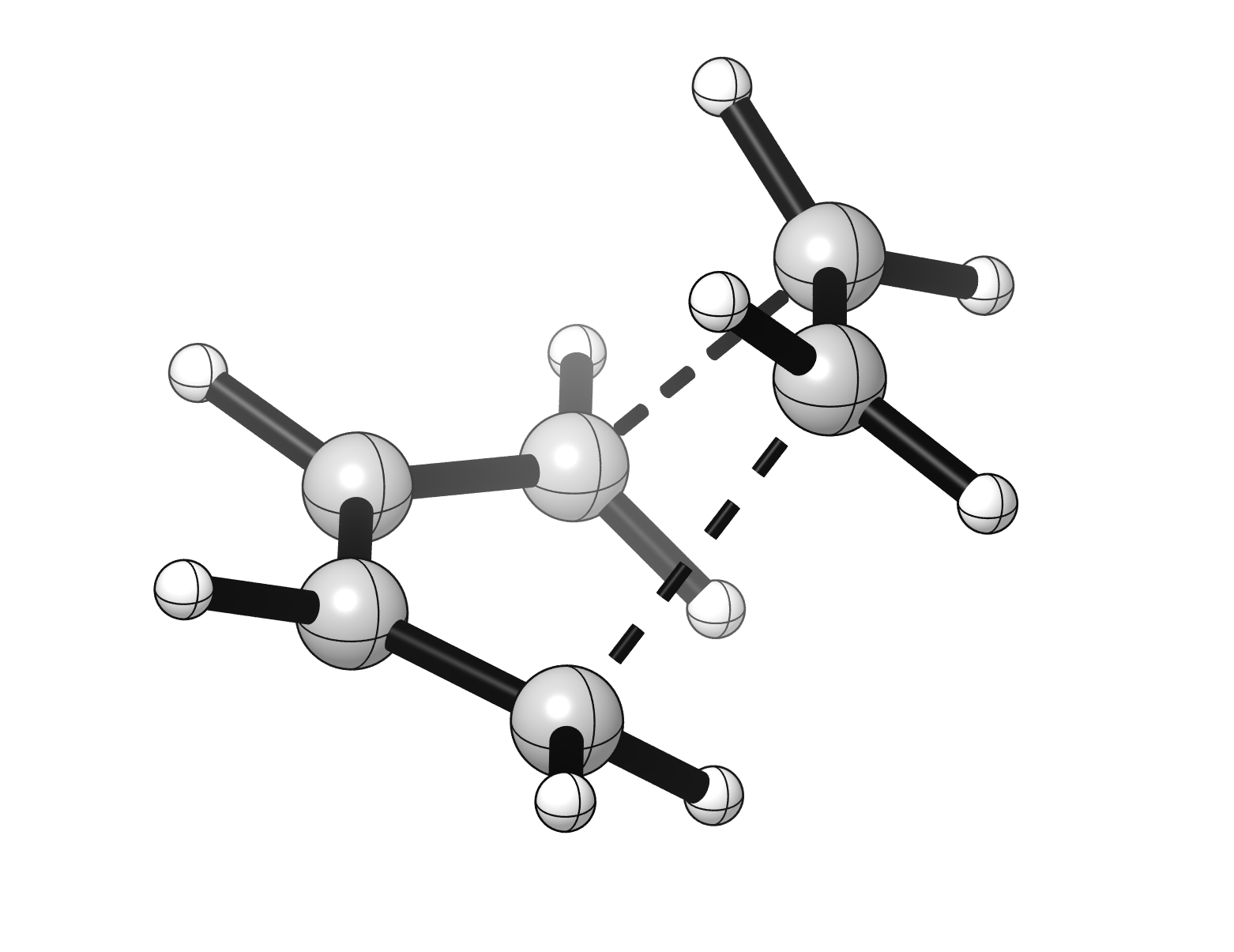
The Diels-Alder reaction is the cycloaddition between a diene and an alkene (or an alkyne), often called dienophile, leading to a cyclohexene product. This reaction in an example of pericyclic reactions, which occur via a concerted transition structure, in which all the bonds are broken and formed in the same step.
The reaction involves the π orbitals of both the diene and the dienophile, which are oriented perpendicularly in regards to the plane of the double bonds. For this reason, the two flat reaction partners need to approach each other “face-to-face”, as shown in the transition structure (TS) below. Also notice how the four carbons atoms involved in making new σ bonds go from an sp2 to a sp3 hybridization as the reaction progresses.
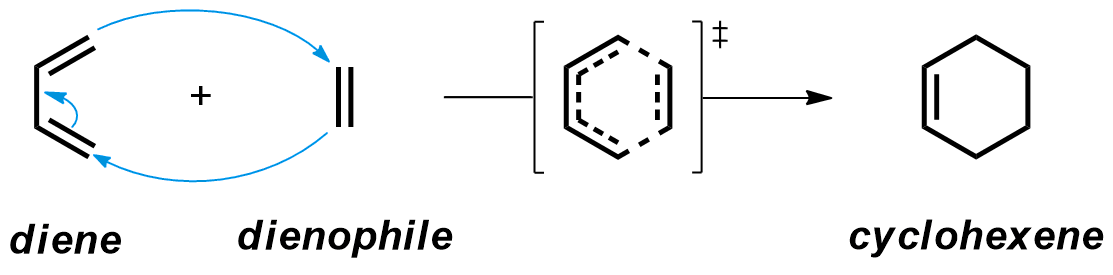

Regioselectivity and diastereoselectivity
When substituted dienes and dienophiles are used, regioisomers and diastereomers may be formed during the reaction. The simplest case involves an electron-rich diene with an electron-donating substituent at the 1-position and an electron-poor dienophile with an electron-withdrawing substituent. In this case, it has been shown that only the 1,2-regioisomer, where the two substituents end up in a 1,2-relationship on the final product, is formed. This effect is due to primary orbital interactions between the most nucleophilic carbon of the diene with the most electrophilic carbon of the dienophile.
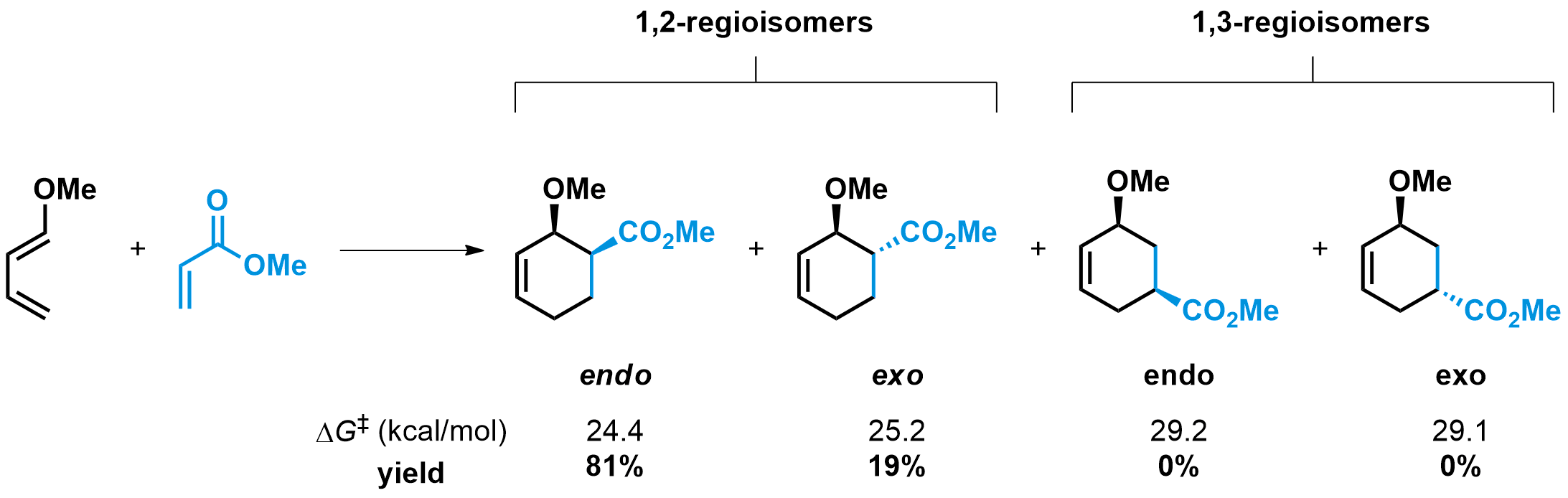
The stereoselectivity of the reaction in such systems often follows the “endo” rule, originating from the favorable secondary orbital interactions possible in the TS leading to the endo product. You can notice in the animation how the ester group of the dienophile remains directly above the diene in the course of the reaction to the endo product, engaging in favorable interactions. For the unfavored exo product, such interactions are not present. Also notice that the cyclohexene product is initially formed in the boat conformation, which will eventually rearrange to the more stable chair conformation

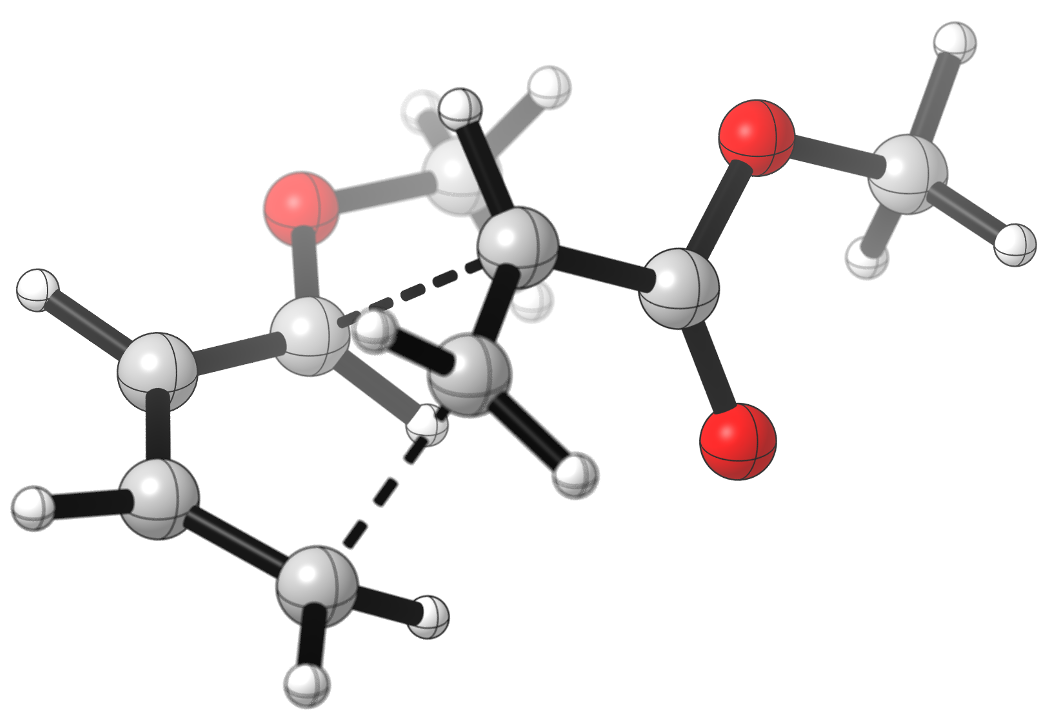
Formation of the major endo product:
Formation of the minor exo product:
Download the data
- Intrinsic reaction coordinate (IRC) file for the parent Diels-Alder reaction. (.xyz)
- IRC file for the endo Diels-Alder of 1-methoxybutadiene with methyl acrylate. (.xyz)
- IRC file for the exo Diels-Alder of 1-methoxybutadiene with methyl acrylate. (.xyz)
Animations created by Floris Buttard.
